In preparation of the upcoming landings of the Mars missions launched in 2020, which are expected to arrive at the red planet in the 1st quarter of 2021, we are going to take a look at Mars Missions that are currently operational. This is not going to be a complete in-depth analysis of each mission, but rather just a quick overview of prior missions that are currently operating. This will help understand how operational missions are working together.
| Name Of Mission | Organizer | Type Of Mission | Launch Date | Arrival Date |
| 2001 Mars Odyssey | NASA | Orbiter | April 7, 2001 | October 24, 2001 |
| Mars Express and Beagle 2 | ESA | Orbiter & Lander | June 2, 2003 | December 3rd, 2003 |
| Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | NASA | Orbiter | August 12, 2005 | March 10, 2006 |
| Curiosity (Mars Science Laboratory) (MSL) | NASA | Rover | November 26, 2011 | August 6, 2012 |
| Mars Orbiter Mission | ISRO | Orbiter | November 5, 2013 | September 24, 2014 |
| MAVEN | NASA | Orbiter | November 18, 2013 | September 22, 2014 |
| ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter | ESA | Orbiter | March 14th, 2016 | October 19th, 2016 |
| Insight | NASA | Lander | May 5th, 2018 | November 26th, 2018 |
For a list of the missions launched towards the red planet in 2020, check out this article.
Mission: Mars Express and Beagle 2
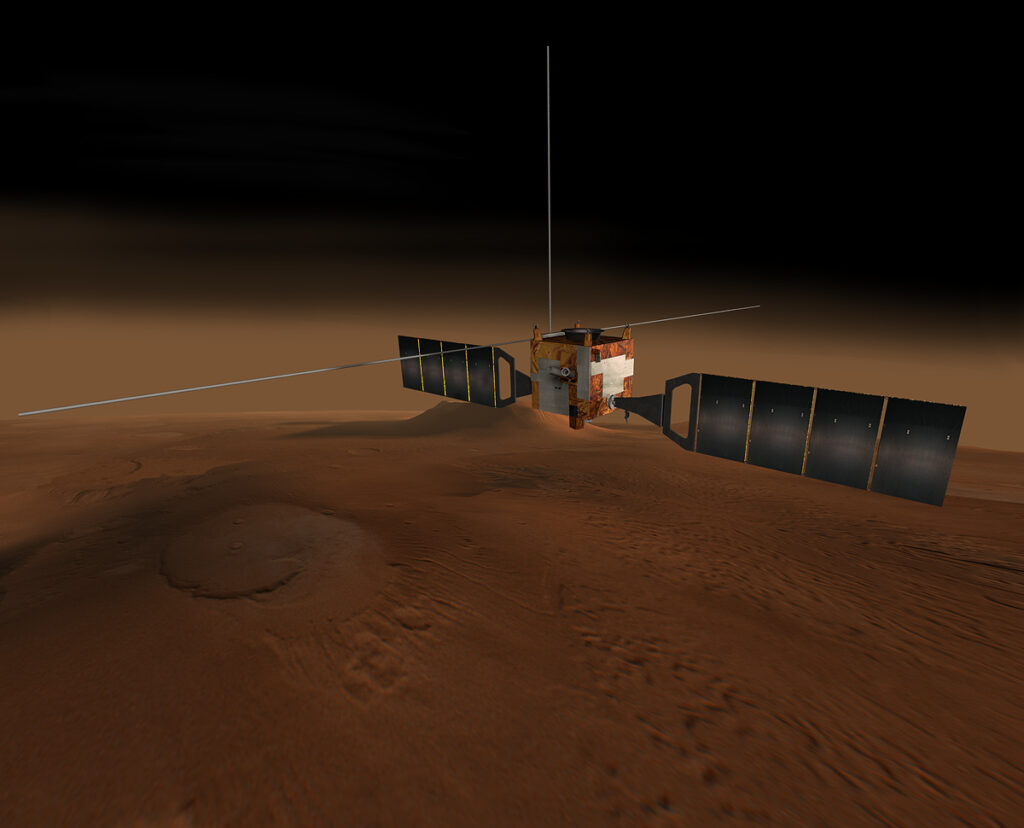
Current Location: In Orbit
Launch: June 2003
Description: This mission consisted of two parts, the Mars Express Orbiter and Beagle 2, a lander designed to perform exobiology and geochemistry research. Although the lander failed to fully deploy after it landed on the Martian surface, the orbiter has been successfully performing scientific measurements since early 2004, namely, high-resolution imaging and mineralogical mapping of the surface, radar sounding of the subsurface structure down to the permafrost, precise determination of the atmospheric circulation and composition, and study of the interaction of the atmosphere with the interplanetary medium.
Mission: Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
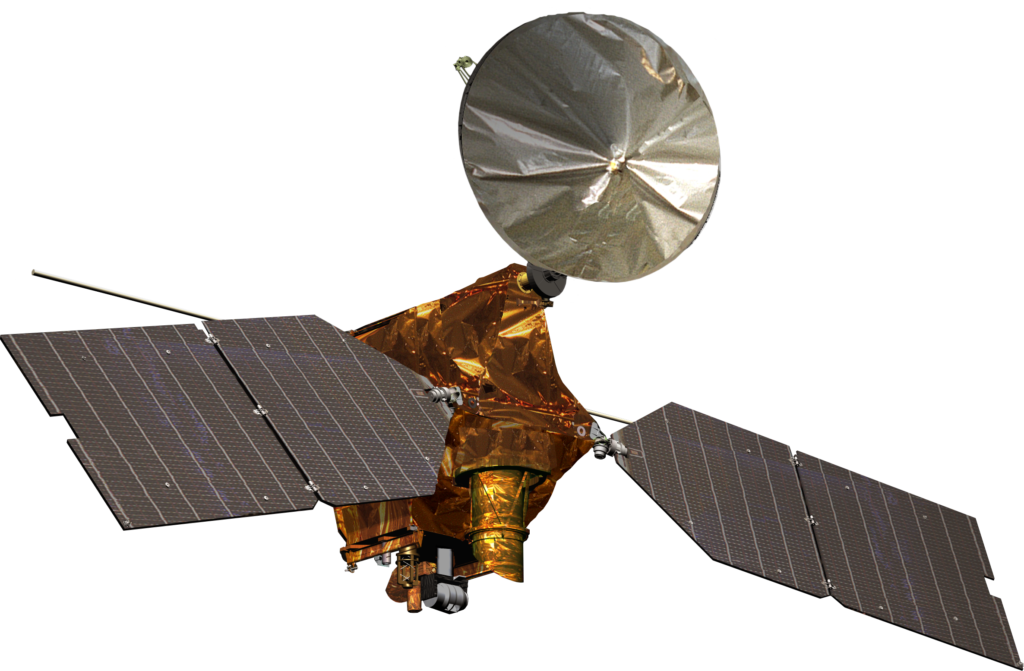

Current Location: In Orbit
Launch: August 2005
Description: This mission is on a search for evidence that water persisted on the surface of Mars for a long period of time. While other Mars missions have shown that water flowed across the surface in Mars’ history, it remains a mystery whether water was ever around long enough to provide a habitat for life.[2] After completing its mission, it has been useful as a relay for landers and orbiters on the planets surface.
Mission: Curiosity
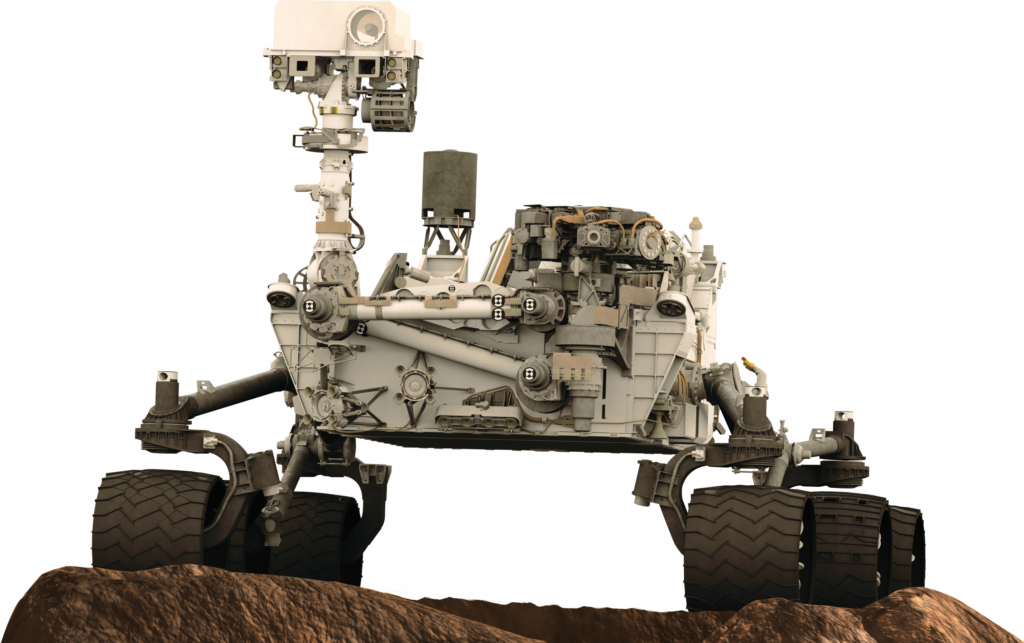
Current Location: On The Surface
Launch: November 2011
Description: Curiosity is a car-sized rover designed to explore Gala Crater. The rover’s goals included an investigation of the Martian climate and geology; assessment of whether the selected field site inside Gale has ever offered environmental conditions favorable for microbial life, including investigation of the role of water; and planetary habitability studies in preparation for human exploration. Curiosity’s rover design served as the basis for NASA’s 2021 Perseverance mission which will carry different scientific instruments and look for life.
Mission: Mars Orbiter Mission
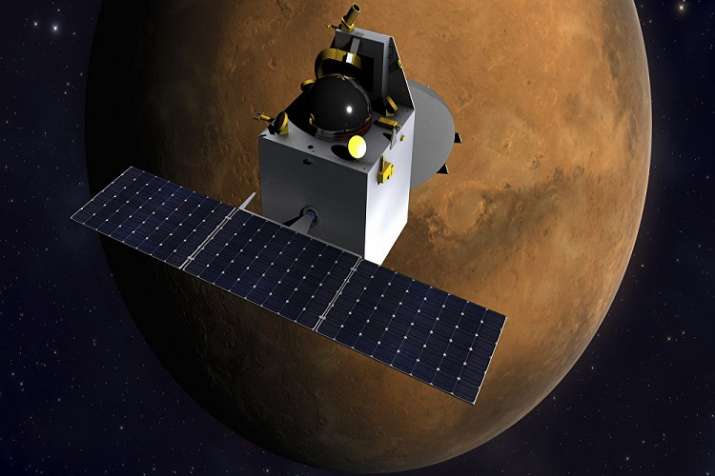

Current Location: In Orbit
Launch: November 2013
Description: Nicknamed MOM, is an orbiting spacecraft by the ISRO, which is their first spacecraft to the red planet. The mission of this orbiter is “to test key technologies for interplanetary exploration and to use its five science instruments to study the Martian surface and atmosphere from orbit.”[3]
Mission: MAVEN
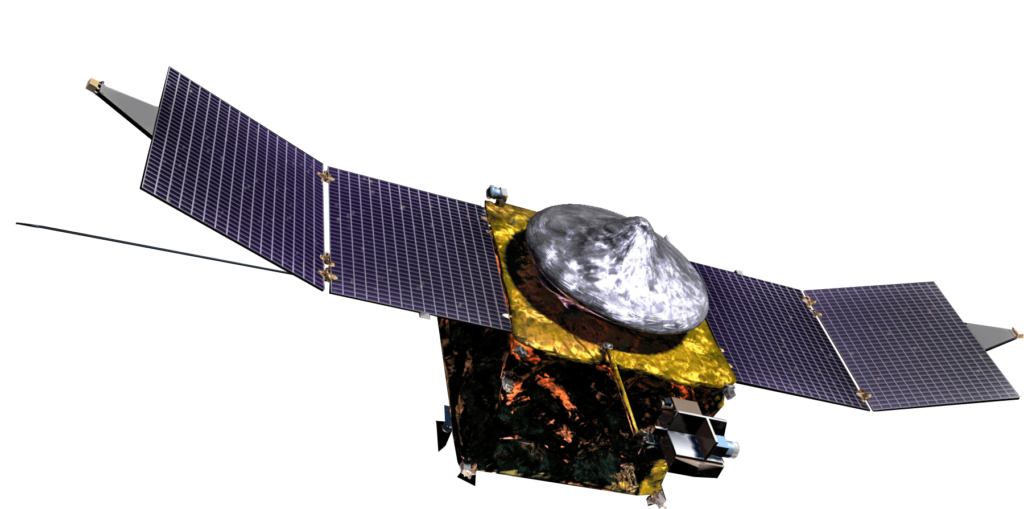

Current Location: In Orbit
Launch: November 2013
Description: The Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution is a spacecraft developed by NASA that went into orbit around Mars to study the planet’s atmosphere. Mission goals include determining how the atmosphere and water, presumed to have once been substantial, were lost over time. A crucial finding has been that the Martian atmosphere has disappeared as a result of solar storms several billion years ago.
Mission: ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter

Current Location: In Orbit
Launch: March 2016
Description: This is an orbiter designed that is currently performing atmospheric research. There was the Schiaparelli demonstration lander that crash landed on the surface. The goal is to gain a better understanding of methane (CH-4) and other trace gases present in the Martian atmosphere that could be evidence for possible biological activity.
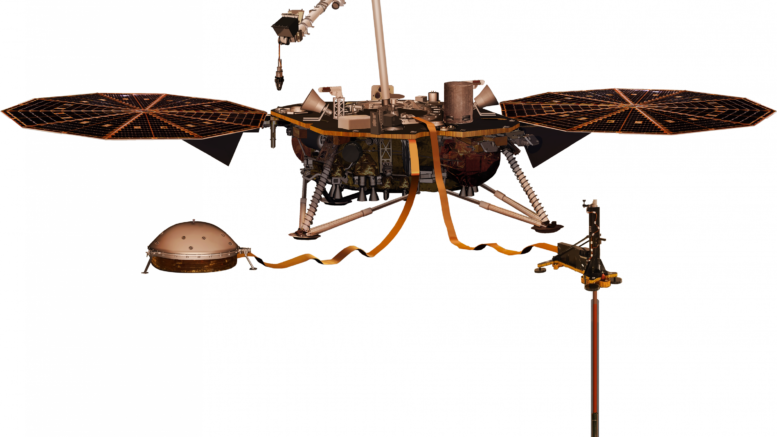
Mission: Insight
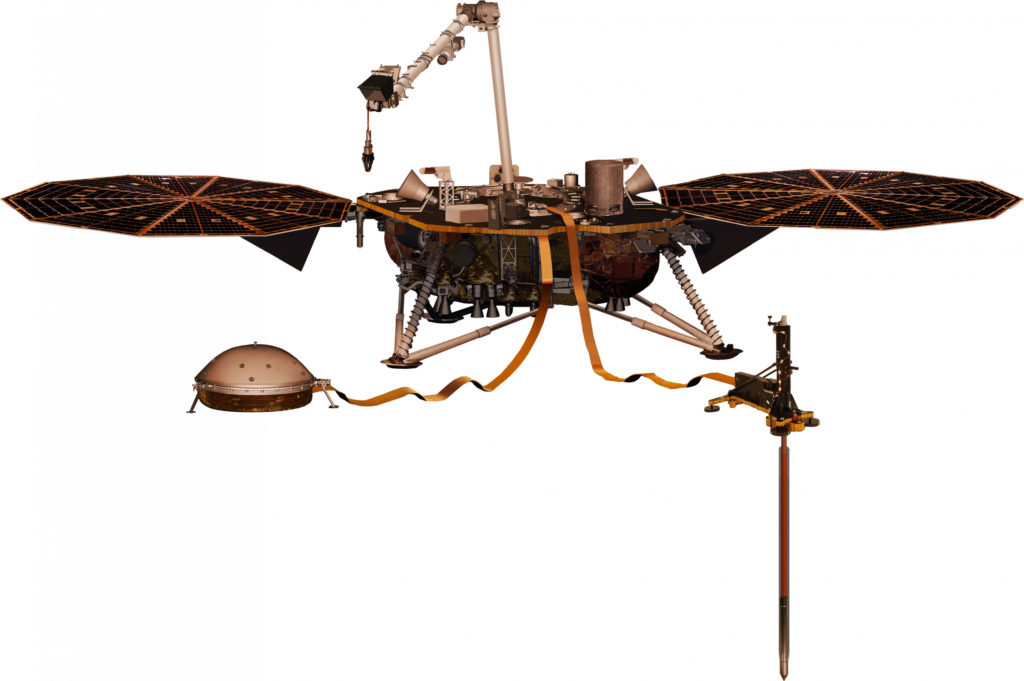

Current Location: In Orbit
Launch: May 2018
Description: This is a mission that is a robotic lander designed to study the deep interior of the planet. The goal of the mission is to study in-depth the “inner space” of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core.[4]
Sources
[1] = https://mars.nasa.gov/mars-exploration/missions/odyssey/
[2] = https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/MRO/mission/index.html
[3] = https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/mars-orbiter-mission/in-depth/
[4] = Insight Mission Page
Leave a comment