Gravitational Waves: An Introduction
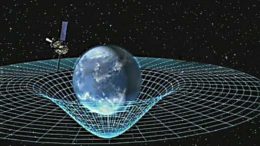
Gravitational Waves can be defined as disturbances in the curvature of spacetime, generated by accelerated masses, that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. This means that gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, which is…