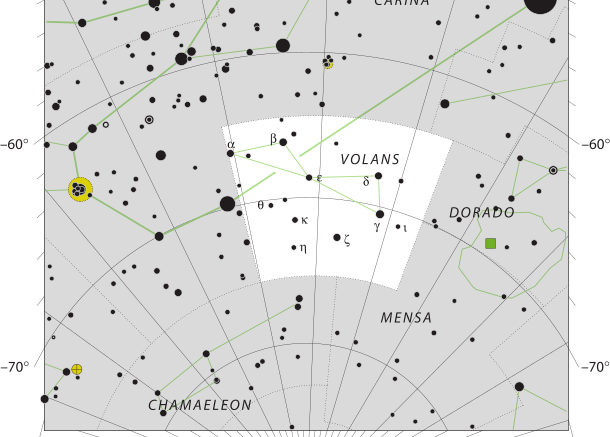
Volans is a constellation in the southern sky that is not visible from the Pacific Northwest. The name Volans is a shortened form of the origin anew of Piscis Volans. Volans was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. The constellation made its first appearance on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 in Amsterdam by Plancius with Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction Volans in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer’s 1603 Uranometria.
Volans represents a type of tropical fish that can jump out of the water and glide through the air on wings. In early celestial maps, the flying fish was often depicted as accompanying the ship Argo Navis, which is being chased by the predatory fish represented by the adjoining constellation Dorado.
| Applicable Information | |
| Visibility In Pacific Northwest | Not Visible In PNW |
| Best Times To View | Not Visible In PNW |
| Right Ascension | 8h |
| Declination | −70° |
| Area | 141 square degrees |
| Main Stars | 6 |
| Brightest Object | β Vol |
| Meteor showers | 0 |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Neighboring Constellations | Carina, Pictor, Dorado, Mensa, Chamaeleon |
History
In the late 16th century, as Europeans were exploring the seas, they made some important discoveries and added 12 new constellations to the list of known constellations. Volans is one of these 12 constellations that were introduced during this time. In the late 16th century, the Dutch navigators Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman first depicted on Petrus Plancius’ globe in 1598. Plancius called the constellation Vliegendenvis, flying fish.
But it wasn’t until 1603, that Volans was first added into star atlases, when Johann Bayer included the constellation in his star atlas Uranometria under the name Piscis Volans, the flying fish. In 1844, the name Piscis Volans was proposed to be shrunk to just Volans by John Herschel, which was then adopted.
Stars
There are two double stars within the constellation which can be observed using small telescopes, Gamma Volantis and Epsilon Volantis. NGC 2442 and NGC 2434 are 2 galaxies can be difficult to see, but might be visible using a small telescope.
Notable deep sky objects include NGC 2442, an intermediate-spiral galaxy, and the Lindsay-Shapley ring, also known as AM0644-741, which is a ring galaxy located 300 million light-years from Earth, near the large magellanic cloud.
Make sure to check out other articles on the site, including a brief introduction to constellations, other constellation articles, and more!
Be the first to comment on "Volans"