This review of Messier 4 is to provide details about the observational history, details about how to find it in the sky, what the object could look like in your scope, and potential astrophotography options if available.
Messier 4 is one of the nearest globular clusters to Earth, and has an age of 12.2 billion years. The stars are loosely tied together.
| Description | |
| Visible From Pacific Northwest | May, June, And July |
| Best Time To Observe | June and July |
| Minimum Size Of Viewing Device | 10×50 binoculars |
| Object Type | Globular Cluster |
| Designations | Messier 4, M4, NGC 6121 |
| Right Ascension | 16h 23m 35.22s |
| Declination | -26°31’32.7” |
| Constellation | Scorpius |
| Absolute magnitude | 11.2 |
| Apparent magnitude | +5.9 |
| Apparent dimensions | 26′.0 |
| Object Radius | 35 light years |
| Distance From Earth | 7,175 light years |
History
M4 was discovered by the Swiss astronomer and mathematician Jean-Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1746, who added it to his catalogue as number 19. Charles Messier catalogued the cluster on May 8, 1764. French astronomer Nicholas Louis de Lacaille discovered the globular cluster independently on April 13, 1752 and included it in his catalogue as Lacaille I.9, noting that “It resembles a small nucleus of a faint comet.”
Fun Fact: M4 was the first and only globular cluster to be resolved into individual stars by Messier himself. Other globulars in the Messier catalogue were not resolved until about 20 years later, when William Herschel observed them in his larger telescope
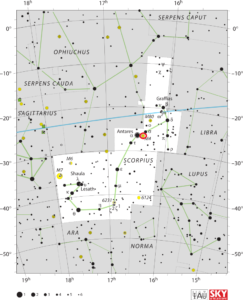
Locating M4 In The Sky
It is one of the easiest globular clusters to find, being located only 1.3 degrees west of the bright star Antares. Please note, if observing in the late spring or summer, make sure to wait for Scorpius’ tail to rise rover the horizon. Moreover, make sure to verify that you are looking at M4, not Mars as Mars might have a similar color.
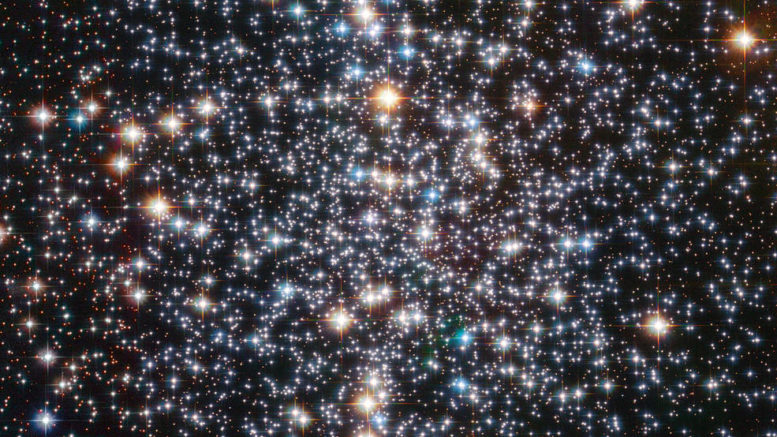
Viewing M4
Messier 4 has roughly the same apparent size as the full Moon. It is visible to the naked eye, but only in exceptionally good conditions. If it weren’t obscured by clouds of dark interstellar dust, the cluster would appear far brighter. In 10×50 binoculars, the core region appears quite bright and is surrounded by a halo of light. In small instruments, M4 appears as a fuzzy patch of light, while medium to large telescopes reveal individual stars and the central bar structure.
Photographing M4
Photographing M4 might be bit tricky because of its location, if it is closed to the horizon at the time of imaging. But the good thing is that with the right camera and tracking equipment, a great image can be captured in as little as 75 minutes of total exposure. With 30 second exposures per frame, that means as few as 150 frames. These frames should be split amongst the different L, R, G, and B filters to get enough shots to process the shots.
Sources And Further Reading
Our reviews of Messier Objects can be found here for those looking for a full list.

Be the first to comment on "Messier 4"