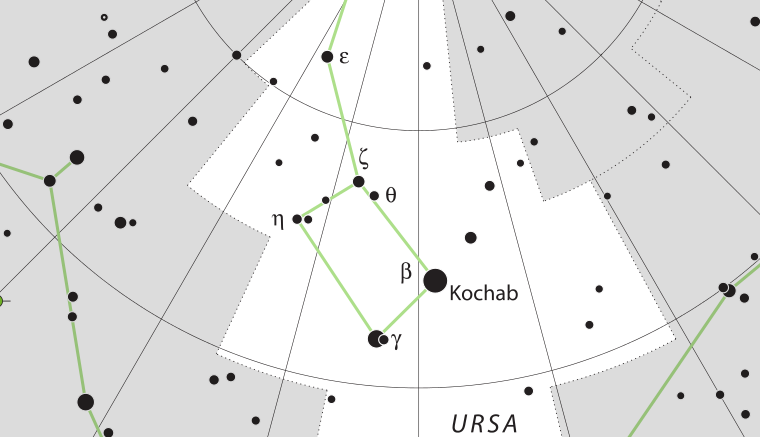
Known as the Little Dipper or Little Bear, the constellation Uraa Minor is located in the far northern sky. Just as with the Big Dipper Asterism, the tail of the Little Dipper may also be seen as the handle of a ladle. This is where the the name Little Dipper comes from. It is composed of seven stars with four in its bowl like its partner the Big Dipper.
The history of Ursa Minor goes back a long time as it was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. It remains one of the 88 modern constellations in the modern sky and throughout history, Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation. This is a result the constellation containing the northern most pole star, Polaris, which was useful for mariners on their sea journeys.
The brightest star in the constellation is Polaris, which is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky. Beta Ursae Minoris, otherwise known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant, which would be only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and 3rd-magnitude Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the “guardians of the pole star” or “Guardians of The Pole”.
As cultures see the skies differently and have different myths, other cultures have other names for this celestial object. For the Babylonian culture, Ursa Minor was known as the “Wagon of Heaven” and Chinese astronomy has the main stars of Ursa Minor divided between two separate asterisms.
Check out this article for more information about asterisms, and make sure to follow us on social media for updates! Articles are posted here weekly, so make sure to come back for more articles like this!
Be the first to comment on "Little Dipper Asterism"