Lying on the plane of the Milky Way, the constellation Cygnus derives its name from the Latinization of the Greek word for swan. Cygnus has become 1 of the most recognizable constellations because of its association with the Northern Cross asterism. Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. Covering 804 square degrees and around 1.9% of the night sky, Cygnus ranks 16th of the 88 constellations in regards to size.
Cygnus contains Deneb, which one of the brightest stars in the night sky and the most distant first-magnitude star. Cygnus is one corner of the Summer Triangle. Cygnus is known as the Northern Cross. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets.
The largest structure in the observable universe, the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall is partially in this constellation.
| Applicable Information | |
| Visibility In Pacific Northwest | June to October |
| Best Times To View | September |
| Right Ascension | 20.62h |
| Declination | +42.03° |
| Area | 804 square degrees |
| Main Stars | 9 |
| Brightest Object | Deneb |
| Meteor showers | October Cygnids, Kappa Cygnids |
| Messier objects | 2 |
| Neighboring Constellations | Cepheus, Draco, Lyra, Vulpecula, Pegasus, Lacerta |
The Name
In Hinduism, Cygnus is related to meditation as it is related to the best time to meditate, which is when Cygnus would be in the sky.
In Polynesia, Cygnus was often recognized as a separate constellation. In Tonga it was called Tuula-lupe, and in the Tuamotus it was called Fanui-tai.
In New Zealand the constellation was called Mara-tea, in the Society Islands it was called Pirae-tea or Taurua-i-te-haapa-raa-manu, and in the Tuamotus it was called Fanui-raro.
The star Deneb was given its name by Islamic astronomers as the name Deneb comes from the Arabic word dhaneb, meaning “tail.”
In Greek mythology, Cygnus has been identified with several different legendary swans. Zeus disguised himself as a swan to seduce Leda, Spartan king Tyndareus’s wife, who gave birth to the Gemini, Helen of Troy, and Clytemnestra; Orpheus was transformed into a swan after his murder, and was said to have been placed in the sky next to his lyre; and the King Cygnus was transformed into a swan.
Stars
Bayer catalogued many stars in the constellation, giving them the Bayer designations from Alpha to Omega and then using lowercase Roman letters to g. John Flamsteed added the Roman letters h, i, k, l and m, but were later dropped by Francis Baily.
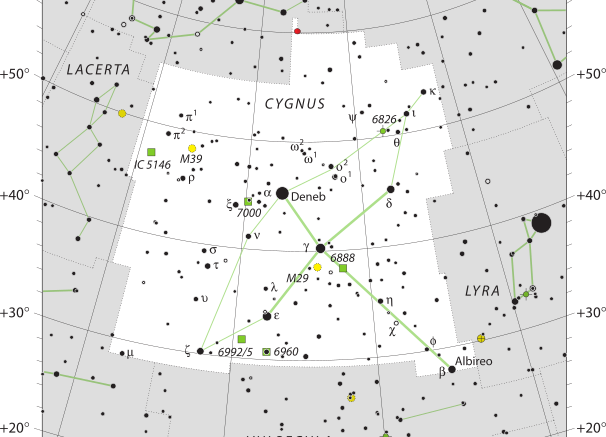
There is an abundance of deep-sky objects, with many open clusters, nebulae of various types and supernova remnants found in Cygnus due to its position on the Milky Way. Some open clusters can be difficult to make out from a rich background of stars.
M39, also known as NGC 7092, is an open cluster that is visible to the unaided eye under dark skies. The open cluster is roughly 30 stars arranged over a wide area; with the appearance being triangular.
NGC 6910, also called the Rocking Horse Cluster, is an open cluster with 16 stars that are visible in a small amateur instrument. A large telescope for amateur astronomers could reveal 8 more stars, bringing the total to 24 stars.
NGC 6826, the Blinking Planetary Nebula, is a planetary nebula with a magnitude of 8.5, which appears to “blink” in the eyepiece of a telescope. The blinking is a result of the unusual brightness of the central star, which is of the 10th magnitude.
The North America Nebula or NGC 7000 is one of the most well-known nebulae because it is visible to the observer under dark skies without an optical device, as a bright patch in the Milky Way. However, the characteristic shape is only visible in long-exposure photographs. Moreover, it is difficult to observe in telescopes because of its low surface brightness.
Make sure to check out other articles on the site, including a brief introduction to constellations, other constellation articles, and more!
Be the first to comment on "Cygnus"