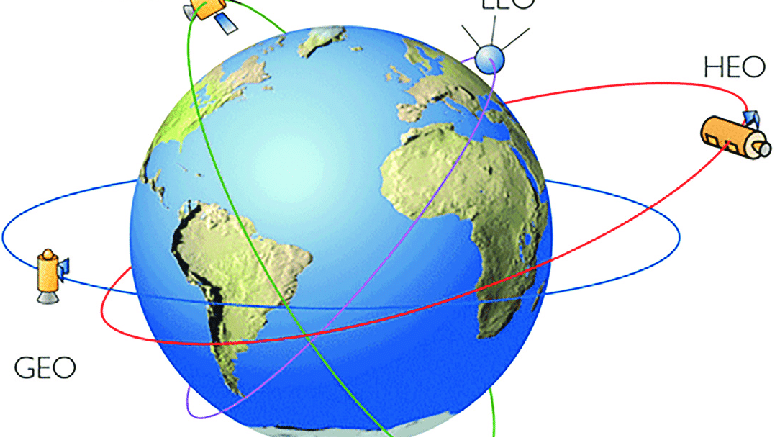
Today, we will be talking about the different satellite orbits that are commonly used. These are the most often used, but not a full list of all the possible orbits.
Geostationary transfer orbit
This is an elliptical Earth orbit used to transfer a spacecraft from a low altitude orbit or flight trajectory to geostationary orbit. The apogee is at 36 000 km. When a spacecraft reaches this point, its apogee kick motor is fired to inject it into geostationary orbit.
Low Earth orbits
A low Earth orbit is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 km and could be as low as 160 km above the Earth. Satellites in this circular orbit travel at a speed of around 7.8 km per second. At this speed, a satellite takes approximately 90 minutes to circle the Earth.
In general, these orbits are used for remote sensing, military purposes and for human spaceflight as they offer close proximity to the Earth’s surface for imaging and the short orbital periods allow for rapid revisits. The International Space Station is in low Earth orbit.
Medium low Earth orbit
This orbit takes place at an altitude of around 1000 km and is particularly suited for constellations of satellites mainly used for telecommunications. A satellite in this orbit travels at approximately 7.3 km per second.
Polar orbits
As the name suggests, polar orbits pass over the Earth’s polar regions from north to south. The orbital track of the satellite does not have to cross the poles exactly for an orbit to be called polar, an orbit which passes within 20 to 30 degrees of the poles is still classed as a polar orbit.
These orbits mainly take place at low altitudes of between 200 to 1000 km. Satellites in polar orbit look down on the Earth’s entire surface and can pass over the North and South Poles several times a day.
Polar orbits are used for reconnaissance and Earth observation. If a satellite is in polar orbit at an altitude of 800 km, it will be travelling at a speed of approximately 7.5 km per second.
Sun synchronous orbits
These are polar orbits which are synchronous with the Sun. A satellite in a sun synchronous orbit would usually be at an altitude of between 600 to 800 km. Generally these orbits are used for Earth observation, solar study, weather forecasting and reconnaissance, as ground observation is improved if the surface is always illuminated by the Sun at the same angle when viewed from the satellite.
Leave a comment